At the end of 2018, AT&T launched the first 5G (or fifth-generation) wireless networks in 12 cities, and while the growth of that industry has been incredible, experts predict that “we ain’t seen nothing yet!” and that the widespread implementation of this technology is happening right now—and through the next 10 years.
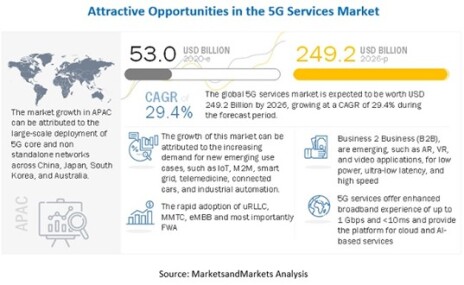
According to Heavy Reading, network providers around the world are forecasted to shell out $88 billion annually by 2023 on 5G network deployment. And MarketsandMarkets.com reports that the global 5G Services Market size is predicted to grow at a 29.4% CAGR, $53.0 billion in 2020 to $249.2 billion by 2026.
The biggest 5G players right now are the U.S. and China. VIAVI says that China has 341 5G-connected cities and the U.S. has 279. That’s growth of six-fold and five-fold, respectively, in just one year! And Ericsson forecasts that by the end of last year there were 220 million 5G subscriptions in China. But Ericsson also believes that by 2026, North America will have 80% of all mobile subscriptions.
[text_ad]
Here’s what the global 5G leaderboard looks like now:
| Country | Number of cities in which 5G is available |
| China | 341 |
| USA | 279 |
| South Korea | 85 |
| UK | 54 |
| Spain | 53 |
| Canada | 49 |
| Australia | 37 |
| Saudi Arabia | 37 |
| Italy | 35 |
| France | 24 |
| Thailand | 24 |
| Sweden | 23 |
(Source: VIVAI)
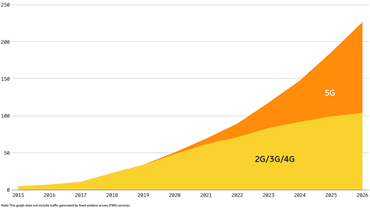
As to telecoms, T-Mobile currently has the best 5G availability, according to Opensignal, with connectivity more than 30% of the time; AT&T, 18%; and Verizon, just 9.5%. There’s a lot more room to grow, as Ericsson says global mobile data traffic will grow by 4.5 times, reaching 226EB (internet traffic) per month in 2026.
Why is 5G Technology Such a Big Deal?
Most people don’t realize that we’ve actually had access to wireless communications for more than a century. But it was only in the late 1970s and early 1980s that it became commercially viable.
It started with 1G, with the advent of cell phones, allowing just mobile voice calls.
Next, the second generation (2G) introduced text messaging (the bane of my existence!), which boosted the growth of the cellular industry.
With the inception of 3G in 1998, media-rich applications like mobile internet browsing and video calling were adopted (growing to speeds up to 4 Mbps.)
Most of us are very familiar with 4G LTE, with its speeds between 10-50 Mbps. 4G has rapidly changed the wireless world, allowing streaming, group video conferencing, mobile online gaming, and augmented and virtual reality.
But as with the other generations, 4G has its limitations, such as buffering, and data latency (the delay before data is transferred), which can drive you nuts when you have a large file to download. While that’s an irritation for most of us, it can be a disaster for industries that require near-instant communications, such as healthcare and transportation, especially autonomous vehicles.
And that’s where 5G steps in. According to CBIInsights, 5G speeds may be as fast as 700-3,000 Mbps (3 Gbps) once the technology becomes commercially available. Their prediction: “Movies that took minutes to download with 4G will take seconds with 5G.”
There are several catalysts driving the launch of 5G technology:
Catalyst No. 1: The Internet of Things (IoT)
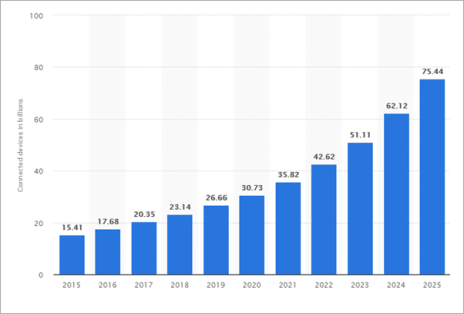
IoT is simply an interconnected network that allows certain ‘smart’ devices to communicate with each other. Those devices include smartphones, smart refrigerators, smart fire alarms, smart door locks, smart bicycles, medical sensors, fitness trackers, surgical robots, electrical grids, navigation systems, smart security systems, smart watches, wearables, buildings, automobiles, and tons of other types of devices. According to Softwaretestinghelp.com, there are more than 20 billion active IoT devices, a number that is expected to surpass 75.44 billion in 2025.
All of these devices are exchanging a lot of data, expected to reach 73.1 ZB (zettabytes) by 2025. Hence, the need for faster and more dependable communications networks like 5G.
And while we all love our IoT devices (most of the time!), we probably don’t think about the economic impact of the industry. It is pretty incredible, with global IoT spending estimated to be $15 trillion between 2019 and 2025.
Catalyst No. 2: Healthcare
Healthcare is going the route of preventative care in order to save costs. And that’s where wearable devices become extremely important. CBI Insights predicts that monitoring, diagnosis, and prevention will rise from 30% to 49% of healthcare spending by 2025. Telemedicine alone is estimated to rise to $86 billion by that year.
Catalyst No. 3: Driverless Cars
In 2016, Qualcomm, Ericsson, Huawei, and Nokia, formed a consortium, the 5G automotive Association (5GAA), to work on “cellular-vehicle-to-everything,” or C-V2X technology.
In the C-V2X system, instead of vehicles deciding how to act individually, they communicate with each other, as well as with traffic lights and construction signs, so that they are safer and more efficient. Consultant Analysys Mason forecasts that the number of automotive 5G connections will reach 96 million by 2027.
It’s estimated that a Google autonomous car produces around 1GB of sensor data per second, adding up to 2 Petabytes of data per year (2 million GB) per car. That’s per year right now, but for future autonomous vehicles, that 2 million gigabytes of data used will be per week, which will require 5G technology.
Catalyst No. 4: Augmented (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Using AR, it’s easy to look up schematics and instructions to repair and maintain equipment, drastically reducing repair times.
Currently, latency, interrupted connections, and rising traffic are making 4G for AR and VR obsolete, so applying 5G will allow both applications to leapfrog over past progress. In 4G, latency is about 200 milliseconds, which will decline to 1 millisecond (1ms) with 5G.
Mordor Intelligence forecasts the AR and VR industries will grow to $296 billion by 2026, with mobile gaining the largest increases.
As you can see by the following graphic, there are opportunities across the world and most industries with the rollout of 5G.
So, I think you can see why 5G is such a big deal, hmm?
No doubt, the advent of 5G technology will eventually affect pretty much every company, no matter the industry. But telecom gurus predict just a few will see immediate benefits, including:
Manufacturing
Manufacturing will benefit from 5G’s higher bandwidth and lower latency, leading to ‘smart’ and safer factories, depending on more automation and IoT connections to improve speed of production, as well as data mining. According to Forbes and Statista, smart factories in North America are expected to be worth more than $500 billion next year, led by consumer electronics and transportation.
One of the big benefits of using 5G technology in manufacturing is slicing—the ability to run multiple dedicated networks on the same infrastructure (shared by multiple tenants) to customize speed, coverage, and security. Consultant Capgemini reports that “more than two-thirds of industrial companies are ready to deploy it within two years of availability.” The cost savings of not having to build individual infrastructures for multiple tenants will be enormous.
Media/Entertainment
If you get frustrated with buffering when you’re streaming, 5G promises to vastly improve that due to its faster capabilities. And with its lower cost per gigabyte, streaming should become more cost efficient. Intel recently commissioned a report that concluded “media and entertainment experiences enabled by 5G will generate up to $1.3 trillion in revenue by 2028.”
Transportation
Have you ever wished you could tell that driver in front of you to just move over? Well, that day is coming. With 5G and IoT technology, vehicles will be able to communicate with each other; sensors will not only tell you that you are drifting in your lane, but will give you information on the other cars in your immediate driving range, and send you traffic and safety alerts, and could even tell you where the closest parking spot is located. In the commercial arena, the faster data collection will help companies schedule freight better and save on fuel.
In addition to autonomous cars, IBISWorld says 5G will impact transportation in three other ways:
- 5G could help increase the flow of traffic with smart traffic management systems, as real-time traffic patterns would be monitored by sensors and cameras.
- Taxi drivers and contract drivers for companies like Lyft and Uber could save money on gas and pick up more passengers, due to increased flow of traffic and a reduction in vehicle wait time.
- 5G could help decrease commute times.
Three 5G Technology Stocks
The 5G investment opportunities will be immense, with scads of cutting-edge companies debuting new products, and eventually, being gobbled up by their larger competition, but those days are still in front of us.
I still feel more comfortable putting our dollars to work in stable companies that have long track records of adapting and innovating as technology changes. I’ve looked at dozens of stocks, and I think the following three companies represent some of the best 5G opportunities right now. And all three have been recently recommended in my Wall Street’s Best Digest newsletter.
Crown Castle International Corp. (CCI). Real estate is a key area for 5G, and cell tower operators like Crown Castle are essential players, as they are required to broadcast 5G signals.
Contributor John Dobosz of Forbes Dividend Investor recommended CCI in our Top Picks for 2021 issue, saying:
“Crown Castle International is a real estate investment trust (REIT) that specializes in communications infrastructure, providing services to wireless carriers through 40,000 cell towers, 70,000 small cell nodes, and 80,000 miles of fiber.
“The towers segment accounts for 70% of the company’s $5.8 billion in annual revenue. Funds from operations (FFO), the most relevant performance metric for REITs, are expected to grow 10.5% in 2021. FFO grew 5.2% last year.”
Crown Castle is partnering with Dish Network for 5G. And in addition to towers, the company makes small-cell radio antennas for 5G services in urban areas, which will connect 5G small-cell sites to the rest of the internet.
Digital Realty Trust, Inc. (DLR), another REIT, is a top developer and acquirer of data centers, with telecom clients that are integral to building the physical assets needed to make 5G possible. Its clients use its centers to access the cloud for storage, processing, and client interaction needs. DLR is one of the pioneers of the industry.
Contributor Tom Hutchinson of Cabot Dividend Investor likes DLR, noting,
“Aside from the long-term advantage of being in a growth business (data center properties), there are a couple of things to like about DLR in the near term. One is that after going sideways for a long time the stock broke out to a new near-term high, which is positive from a technical perspective. The other is that it’s a fantastic stock to own in turbulent markets. It has a microscopic beta of just (0.30), meaning that it tends to move independently of the overall market. It’s good to have a stock like that in the portfolio, especially as things get a little dicey.”
The company has increased its dividend for the last 16 years—a nice extra to accompany the growth ahead.
NVIDIA Corporation (NVDA) makes graphics processing units (GPUs), mostly used in high-end video games, but they are also being used for many other applications that require faster download speeds with the ability to accommodate higher traffic—like 5G.
Early last year, the company reported that researchers were using the company’s processors to develop artificial intelligence that could use machine learning more efficiently for growing out the 5G network, saying that, “We have found that for some very hard telecom problems, there’s no math formulation, but AI can learn the problem models automatically, enhancing our GPU-based parallel solutions.”
Contributor Jon Markman, editor of Pivotal Point, commented, “NVIDIA makes the powerful deep-learning infrastructure that is becoming foundational to the development of AI.
“During Q4, the company had $5 billion in sales, the first in its 22-year history. The 61% year-over-year growth in the quarter mirrors spectacular full year sales of $16.7 billion, up 53%. And profits rose 53% to almost $1.5 billion.
“All of this was planned. Under CEO Jensen Huang, NVIDIA has been forging ahead with a larger plan to bring the company’s expertise in graphics to hyperscale data centers. Today, its CUDA software, Mellanox switches, cables and adaptors and continually evolving line up of high-performance graphics processing units are commonplace in cloud computing.
“Investors should consider taking advantage of the current NVIDIA share price weakness. It most likely will not persist.”
As 5G evolves and the winning technologies develop, I’ll be reviewing some of the smaller players in the market, so stay tuned for my updates. In the meantime, these three 5G technology stocks will be a good start to our foray into what will prove to be one of the most exciting—and profitable—investment sectors of our lifetimes.
Do you own any 5G technology stocks? Tell us about them!
[author_ad]
*This post has been updated from an original version, published in 2018.