What about a strategy for bearish markets?
Most traders or investors either short stock, which has undefined risk and can be capital intensive, or simply buy puts. However, in my opinion, a poor man’s covered put options strategy is a far superior way to take on a bearish position while defining you risk and using significantly less capital.
The trade mechanics of a poor man’s covered put is similar to that of a poor man’s covered call, but rather than using calls we use puts.
Let’s go through an example step-by-step so we have a sound understanding on how a poor man’s covered put works in the real world.
Conceptually, poor man’s covered puts are similar to covered puts, with only a few exceptions.
Again, the main difference: poor man’s covered puts require far less capital. The strategy doesn’t require shorting 100 shares of stock. In fact, no shares are needed.
In most cases, it costs 65% to 85% less to use a poor man’s covered put options strategy. The savings in capital required should be reason enough to at least consider using the strategy. And I’m certain after reading this you will indeed find the options strategy appealing.
A poor man’s covered put is an inherently bearish options strategy. But again, rather than spend an inordinate amount of money to short at least 100 shares of stock, and have theoretically undefined risk, you have the ability to buy what is essentially a stock replacement. The replacement? An in-the-money LEAPS put contract.
LEAPS, or long-term equity anticipation securities, are options with at least one year left until they are due to expire. The reason we choose to use LEAPS as our stock replacement is because LEAPS don’t suffer from accelerated time decay like shorter-dated options.
The initial barrier to entry when it comes to selling poor man’s covered puts is security selection. Simply stated, implied volatility (IV) is one of the main keys to security selection. Implied volatility tells us how much risk and return we should expect to see over a 20- to 45-day time frame, so that we can form a realistic plan for creating monthly income.
Next is the price of the security. Just because the IV of a stock fits within our range doesn’t mean that the stock works. We must be able to establish a position while maintaining proper position size in our overall portfolio.
My preference is to buy a LEAPS (put) with a delta of roughly 0.80 and sell puts with a delta between 0.20 and 0.40. The reason is I want to give myself the ability to make some decent returns on my LEAPS contract if indeed the stock pushes significantly lower. My goal is to initiate my poor man’s covered put position with an overall delta of approximately 0.50.
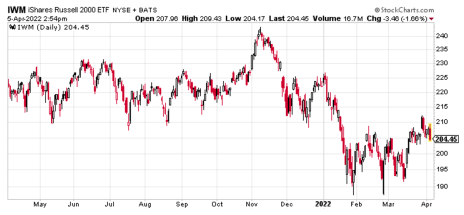
If we followed the route of the traditional covered put, we would need to short at least 100 shares of IWM. At the current share price, shorting 100 shares would cost a minimum of $20,445. For some investors, the cost of 100 shares is prohibitive, especially if diversification amongst a basket of stocks is a priority. Therefore, a covered put strategy just isn’t in the cards.
But, as I said before, with a poor man’s covered put strategy you can typically save 65% to 85% of the cost of a covered put strategy, making it far more affordable.
So again, rather than shorting 100 shares or more of stock, we only have to buy one LEAPS put contract for every 100 shares we wish to control.
If we go with the longest-dated expiration cycle in IWM we are left with the January 19, 2024 expiration cycle with 654 days until expiration.
You can see the expiration cycles currently offered for IWM below.
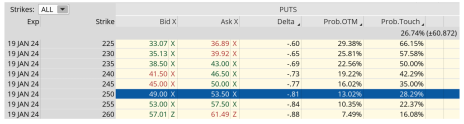
Once I have chosen my expiration cycle, in this case the January 19, 2024, I then look for an in-the-money put strike with a delta of around 0.80.
When looking at IWM’s option chain I quickly noticed that the 250 put strike has a delta of 0.81. The 250 put strike price is currently trading for approximately $51.50. Remember, always use a limit order. Never buy an option at the ask price, which in this case is $53.50.
So, rather than spend $20,445 for control of 100 shares of IWM, we only need to spend $5,150. As a result, we are saving $15,295, or 74.8%. Now we have the ability to use the capital saved to diversify our premium or income stream amongst other securities, if we so choose.
After we purchase our LEAPS put option at the 250 put strike, we then begin the process of selling short-term puts against our LEAPS. This will allow us to not only create a steady income stream, but also lower the cost basis of our overall position.
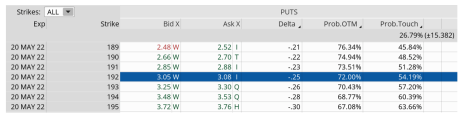
My preference is to look for an expiration cycle with around 30-60 days left until expiration and then aim for selling a put strike with a delta ranging from 0.20 to 0.40, or a probability of success between 60% to 85%.
As you can see in the options chain below, the 192 put strike with a delta of 0.25 falls within my preferred range.
We can sell the 192 put option for roughly $3.06.
Our total outlay for the entire position now stands at $4,844 ($5,150 – $306). The premium collected is 5.94% over 44 days—a decent amount of premium, especially if you consider we are only going out 44 days.
Basically, every 45 days we can collect roughly 5% by selling premium. Conservatively, we can do type of trade 8 times. If so, we would be able to lower the cost basis of our LEAPS position by roughly 40% over the course of one year.
And remember, the 5.94% is just the premium return, it does not include any increases in the LEAPS contract if the ETF pushes lower. Moreover, we can continue to sell puts against our LEAPS position until there is roughly 10 to 12 months of life left in the LEAPS, thereby generating additional income or lowering our cost basis even further.
As an aside, an alternative way to approach a poor man’s covered put if you are a bit more bearish is to buy two LEAPS for every put sold. This will increase the delta of our overall position and allow you to benefit from the additional downside past your chosen short put strike, yet still participate in the benefits of selling premium. I find this method the most effective, as oftentimes if a strong bearish move occurs your position isn’t entirely inhibited by your short put.
Regardless of your approach, you can continue to sell puts against your LEAPS as long as you wish. Whether you hold a position for one expiration cycle or 12, poor man’s covered puts give you all the benefits of a covered put for significantly less capital.
Poor Man’s Covered Put Trade:
- Buy iShares Russell 2000 (IWM) January 19, 2024 250 LEAPS put contracts for roughly $51.50
- Sell iShares Russell 2000 (IWM) May 20, 2022 192 puts (44 days until expiration) for $3.06, or $306 per contract
Static or Return on Premium: 5.94% over 44 days, or 47.52% annually
Initial Breakeven: $48.44, or $4,844
So, as you can see above, we have the potential to create 5.94% every 44 days, or approximately 47.52% a year, using IWM as our underlying.
As always, if you have any questions regarding poor man’s covered puts or anything else covered in this report please do not hesitate to email me at Andy@CabotWealth.com.